Human metabolism has evolved to become energetically unique Biology Diagrams
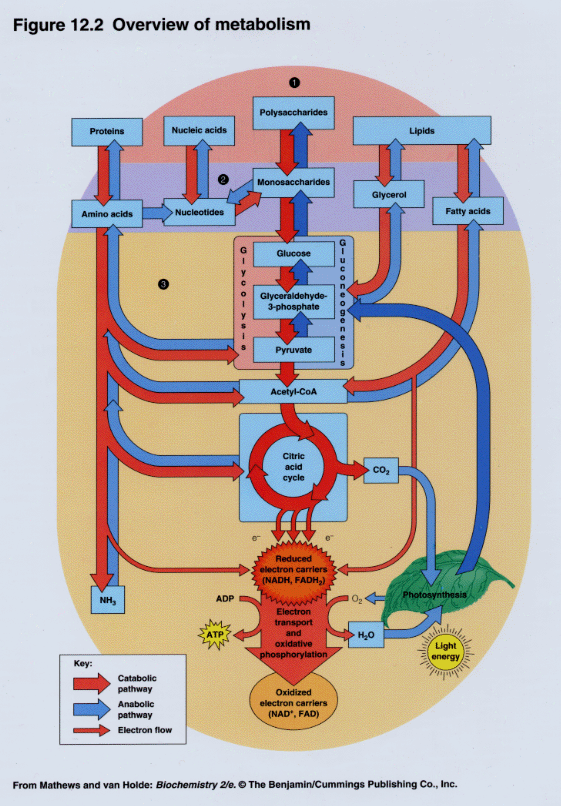
Human metabolism has evolved to become energetically unique Biology Diagrams Metabolism, the sum of chemical reactions that take place in living cells, providing energy for life processes and the synthesis of cellular material. Living organisms are unique in that they extract energy from their environments via hundreds of coordinated, multistep, enzyme-mediated reactions. Metabolism is the sum of all the chemical reactions that are involved, and we can see a glimpse of what is going on in the cells from the following partial map of the human metabolic pathways.

Explore the intricate dynamics of cellular metabolism, focusing on its structure, roles, and interactions within biological systems. Metabolism refers to the whole sum of reactions that occur throughout the body within each cell and that provide the body with energy. This energy gets used for vital processes and the synthesis of new organic material. Every living organism uses its environment to survive by taking nutrients and substances as building blocks for movement, growth, development, and reproduction. All of these Metabolic processes are constantly taking place in the body. Metabolism is the sum of all of the chemical reactions that are involved in catabolism and anabolism. The reactions governing the breakdown of food to obtain energy are called catabolic reactions. Conversely, anabolic reactions use the energy produced by catabolic reactions to synthesize larger molecules from smaller ones, such as
Metabolism: What It Is, How It Works & Disorders Biology Diagrams
Chapter 24 Introduction 24.1 Overview of Metabolic Reactions 24.2 Carbohydrate Metabolism 24.3 Lipid The human endocrine system is like a talented orchestra, harmonizing multiple instruments to produce the beautiful melody of metabolism. From insulin's regulating effects on blood sugar to the thyroid's influence on energy levels, each hormone plays its part.

You will examine the various chemical reactions that are important to sustain life, including why you must have oxygen, how mitochondria transfer energy, and the importance of certain "metabolic" hormones and vitamins. Metabolism varies, depending on age, gender, activity level, fuel consumption, and lean body mass.
