Gcse biology revision Cell division Biology Diagrams
Gcse biology revision Cell division Biology Diagrams Eukaryotic DNA replication is regulated to ensure all chromosomes replicate once and only once per cell cycle. Replication begins at many origins scattered along each chromosome. Except for budding yeast, origins are not defined DNA sequences and probably are inherited by epigenetic mechanisms. Init … When a cell divides, it is important that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the DNA. This is accomplished by the process of DNA replication. The replication of DNA occurs during the synthesis phase, or S phase, of the cell cycle, before the cell enters mitosis or meiosis. DNA replication's primary purpose is to enable living organisms to reproduce. The only way to replace the cells is to copy the cell's information. It is what DNA replication does. After cell division by mitosis or meiosis, the two daughter cells must contain the same genetic information, or DNA, as the parent cell. Without the accurate

Within eukaryotes, DNA replication is controlled within the context of the cell cycle. As the cell grows and divides, it progresses through stages in the cell cycle; DNA replication takes place during the S phase (synthesis phase). The progress of the eukaryotic cell through the cycle is controlled by cell cycle checkpoints. A working model of DNA replication under cell cycle control has resulted (Figure 1b). However, a fully reconstituted in vitro replication system in which both initiation and elongation occur with all purified components is still lacking. Given all the tools of modern, recombinant DNA technology, this issue should be resolved in the future.
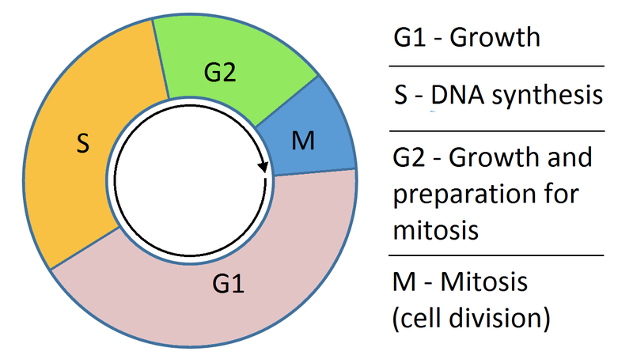
An Overview of the Cell Cycle Biology Diagrams
The most basic function of the cell cycle is to duplicate accurately the vast amount of DNA in the chromosomes and then segregate the copies precisely into two genetically identical daughter cells. These processes define the two major phases of the cell cycle. DNA duplication occurs during S phase (S for synthesis), which requires 10-12 hours and occupies about half of the cell-cycle time in The cell cycle is a series of events that cells go through to grow, replicate their DNA, and divide. This process is vital for the growth, development, repair, and maintenance of living organisms. The synthesis phase is where DNA replication occurs. G 2 phase: Cells continue growing and preparing for mitosis and the cell checks that DNA In contrast, DNA replication in most eucaryotic cells occurs only during a specific part of the cell division cycle, called the DNA synthesis phase or S phase (Figure 5-34). In a mammalian cell, the S phase typically lasts for about 8 hours; in simpler eucaryotic cells such as yeasts, the S phase can be as short as 40 minutes.
