cell cycle check points Biology Diagrams
cell cycle check points Biology Diagrams Checkpoints tightly regulate the cell cycle to prevent errors. These checkpoints include: G 1 Checkpoint: This checkpoint ensures that the cell has adequate energy resources and that the surrounding environment is favorable for DNA replication. If conditions aren't right, the cell can exit to G 0 phase. G 2 Checkpoint: Before entering mitosis

The G 1 Checkpoint. The G 1 checkpoint determines whether all conditions are favorable for cell division to proceed. The G 1 checkpoint, also called the restriction point (in yeast), is a point at which the cell irreversibly commits to the cell division process. External influences, such as growth factors, play a large role in carrying the cell past the G 1 checkpoint.

Cell Cycle: Definition, Phases, Regulation, Checkpoints Biology Diagrams
The Hammer and the Dance of Cell Cycle Control. Andreas Panagopoulos, Matthias Altmeyer, in Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 2021. Cell cycle checkpoints secure ordered progression from one cell cycle phase to the next. They are important to signal cell stress and DNA lesions and to stop cell cycle progression when severe problems occur. Cell cycle checkpoints are control mechanisms that hold the progression of the cell cycle to the next stage in the cell cycle until the conditions are favorable. They ensure proper cell division. The three most important cell cycle checkpoints are the G 1 checkpoint, the G 2 checkpoint, and the spindle assembly checkpoint. G1 checkpoint checks the presence of sufficient raw materials while G 2 Importance of cell cycle checkpoints and regulation. The cell cycle of each cell must be precisely controlled and timed to faithfully and reproducibly complete the developmental program in every individual. Each type of cell in every tissue must control its replication precisely for normal development of complex organs such as the brain or the
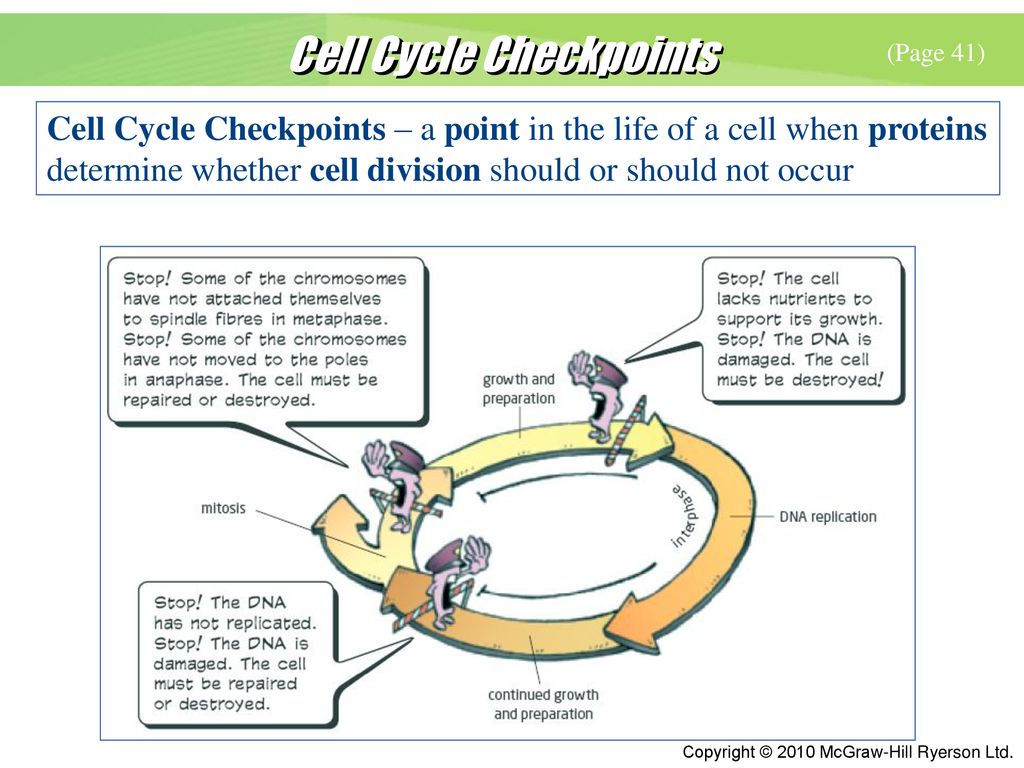
The G1 checkpoint is the first checkpoint in the cell cycle of a mammalian cell and the start point in the yeast cell that determines whether the cell enters the cell cycle or not. Because of the proteins involved in the checkpoint, the G1 checkpoint is an important checkpoint during tumor suppression and prevention of excessive cell Control of the Cell Cycle. The length of the cell cycle is highly variable, even within the cells of a single organism. In humans, the frequency of cell turnover ranges from a few hours in early embryonic development, to an average of two to five days for epithelial cells, and to an entire human lifetime spent in G 0 by specialized cells, such as cortical neurons or cardiac muscle cells.

Cell cycle, Checkpoints, Cyclins and Its Types: Introduction, External ... Biology Diagrams
The cell cycle checkpoints play an important role in the control system by sensing defects that occur during essential processes such as DNA replication or chromosome segregation, and inducing a cell cycle arrest in response until the defects are repaired. [8]
