Anatomy and physiology of the blood Biology Diagrams
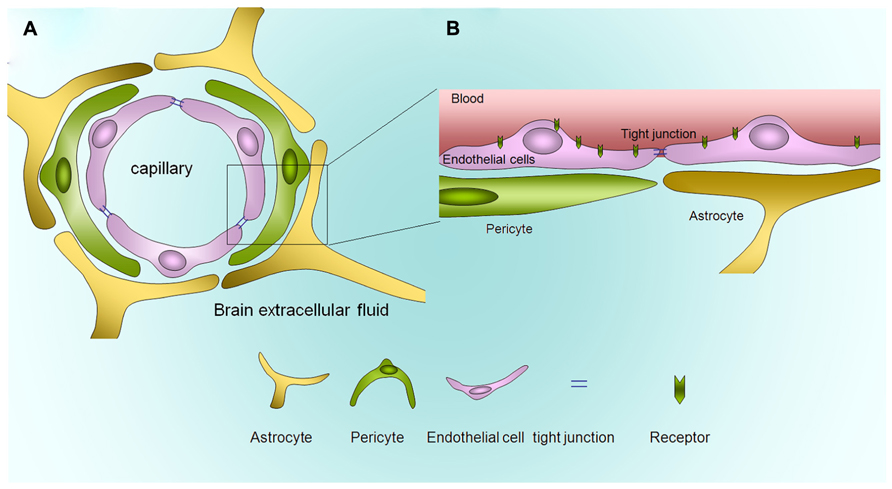
Anatomy and physiology of the blood Biology Diagrams Overview of Blood-Brain Barrier: Anatomy. The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a dynamic interface between the peripheral circulation and the central nervous system (CNS). The basic element of the BBB, the neurovascular unit, is a complex structure composed of capillary endothelial cells (ECs), astrocytes, pericytes, and neurons. The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a selective semi-permeable membrane between the blood and the interstitium of the brain, allowing cerebral blood vessels to regulate molecule and ion movement between the blood and the brain.[1] The BBB is composed of endothelial cells (ECs), pericytes (PCs), capillary basement membrane, and astrocyte end-feet, all of which aim to shield the brain from toxic

Anatomy and Function of the Blood-Brain Barrier. The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a complex and highly selective interface between the circulatory system and the central nervous system (CNS). Its primary role is to protect the brain by regulating the passage of substances and maintaining the optimal environment for proper brain functioning

Physiology, Blood Brain Barrier Biology Diagrams
Blood-brain barriers Definition. Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) is a selectively permeable membrane regulates the passage of a multitude of large and small molecules into the microenvironment of the neurons. It achieves this feat by with the aid of multiple cellular transport channels scattered along the membrane. These include: amino acid transporters

The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a diffusion barrier, which impedes influx of most compounds from blood to brain. Three cellular elements of the brain microvasculature compose the BBB-endothelial cells, astrocyte end-feet, and pericytes (PCs). Blood-Brain Barrier / anatomy & histology* Blood-Brain Barrier / metabolism* Blood-Brain Barrier The blood-brain barrier (BBB), first described by Paul Ehlrich (1885), is a highly selective semi-permeable membrane between the blood and brain interstitium. Anatomy, Head and Neck: Blood Brain Barrier. Dotiwala AK, McCausland C, Samra NS. StatPearls. 2025 Jan. Anatomy, Head and Neck, Larynx Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve. [StatPearls. 2025]
Brain Barrier: Understanding the Brain's Natural Defense ... Biology Diagrams
Location of barrier sites in the CNS. Blood enters the brain via surface arteries (red arrow, top). Barriers between blood and neural tissue are present at three main sites: (1) the brain endothelium forming the blood-brain barrier (BBB), (2) the choroid plexus epithelium which secretes cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and (3) the arachnoid epithelium forming the middle layer of the meninges.
